Data reconstruction
Data measured at site masts typically have gaps when sensors are malfunctioning or have incorrect readings (e.g. when sensors are affected by icing) that are cleaned from the raw data. Gaps in the data can usually be reconstructed using other signals at the same or other measurement sites. The goal is to produce time series with the highest data coverage and lowest uncertainty.
Direction reconstruction
Direction trends are calculated between the time series to reconstruct and the reference series. The direction trends are then applied to the reference direction series to fill any gaps in the series to reconstruct.
Parallel measurement combination
If wind speed sensors are installed in a way so that they are affected by the mast wake, another wind speed sensor installed at the same height on a boom with a different orientation can be used to combine both wind speed signals to remove mast wake effects and increase data coverage. Both wind speed signals require the orientation of the boom that they are installed on and the width of the direction sector to exclude to remove mast shadow effects.
- First we may choose to pre-synthesize data before the directional splice: Wind speed correlations are calculated between the two wind speed measurements and wind speed data are synthesised and spliced to fill any gaps possible. This step reduces bias in the directionally spliced output for records where one measurement has missing data because the wind speed speedup relationship between dual anemometers usually varies smoothly by direction. This step is optional.
- Then the two wind speed signals are directionally spliced based on a direction measurement to create a new wind speed measurement:
- If a record for one wind speed series is missing take the data from the other
- If the wind direction for a record falls within a low priority zone for one wind speed, the output wind speed is equal to the other.
- For all other directions, the output wind speed record is the average of the two input wind speed records.
Speed reconstruction
Wind speed measurement data can be reconstructed from measurements at other heights or masts to increase data coverage. This is usually balanced by the uncertainty introduced by using other to fill gaps or extend the overall data period.
Wind speed correlations are calculated for the series to reconstruct and the reference data. The resulting wind speed trends are applied to the reference data and those are spliced into the series to reconstruct whenever there are gaps in the series to reconstruct.
Synthesis checks
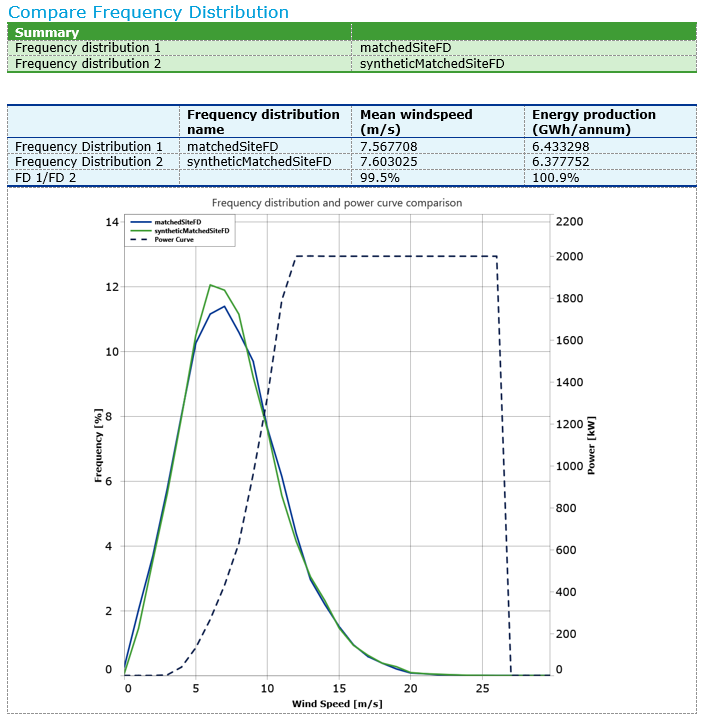
A synthesis check provides a simple check on the quality of the data reconstruction by comparing the synthetic site time series matched with the measured site time series. For a wind speed synthesis check we compare the annual wind speed and energy content of 2 frequency distributions derived fom the synthetic site wind speeds matched with the measured site wind speeds.
Generating a report provides the graphics and data below:
To evaluate the quality of a reconstruction option we recommended that you look at the frequency distribution comparison in the context of the power curve as well as the wind speed and energy ratios because the single value error metrics can hide important differences.
Automation
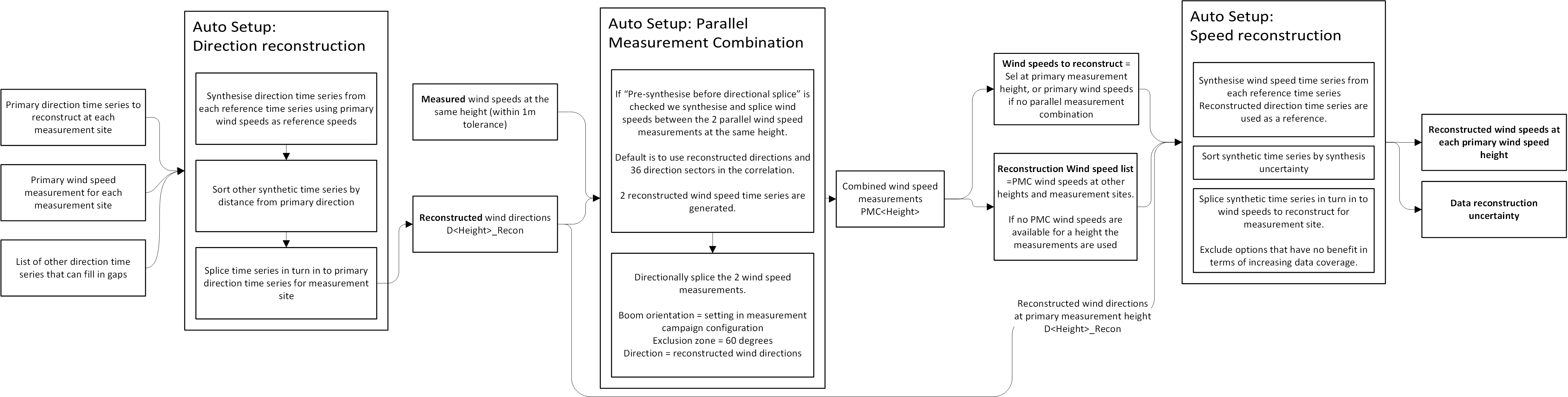
The reconstruction steps can either be set up manually or automatically. The automated optimised data reconstruction workflow is shown below (click image to expand.)