Turbine interaction settings
The 'Turbine interaction settings' task allows the user to define large wind farm correction, wake model and blockage model settings which apply to flow calibration tuning, frequency domain AEP and power time series calculation.
Turbine interaction model
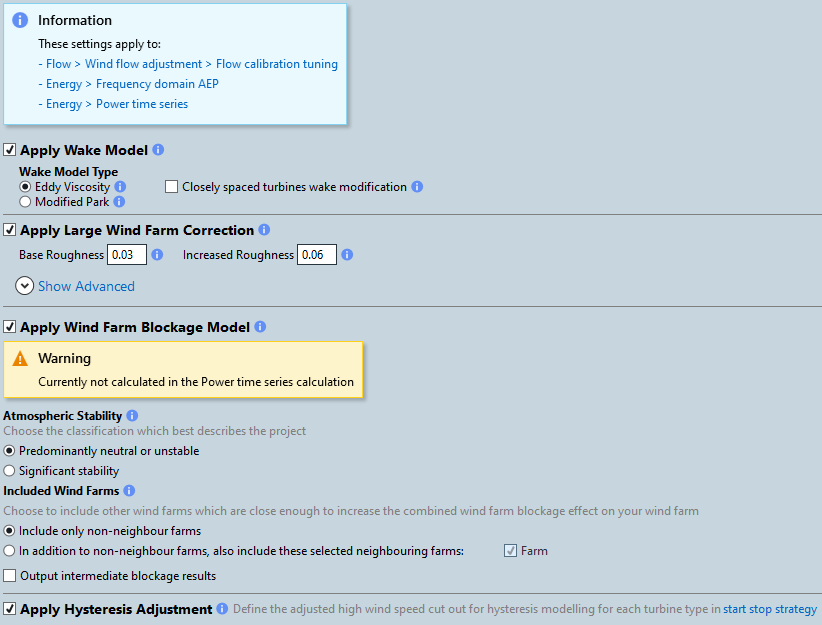
Apply the Large Wind Farm Correction to consider interaction losses with the free flow inside large wind farms or between wind farm clusters. The base roughness should be equal to the average roughness of the wind farm site following the Davenport convention (also used by WAsP). The increased roughness should be equal to the base roughness + 0.03 in most cases. In some cases of high atmospheric stability wakes decay more slowly and a higher additional factor should be used. Different settings may also be used offshore. DNV regularly validate the WindFarmer wake model to refine the settings used in energy production assessments. If you have WasP available, you may calculate base roughness via scripting.
Select either the Eddy Viscosity or Modified Park wake model to consider turbine interaction losses due to wakes caused by individual turbines. As the Eddy Viscosity model is more sophisticated, it is recommended to use this in the energy calculation. The Park model is a simpler model that is faster to run so it is recommended to use this when running layout optimisations.
Apply the Wind Farm Blockage Model to consider effects wind farms have on the upstream ambient flow.
Apply hysteresis adjustment to consider hysteresis adjusted wind speeds for each turbine type. If "Calculate Efficiencies" is enabled, hysteresis effects are reported separately.